Click for detailed diagram Total Solar Eclipse of July The eagerly awaited total solar eclipse of July 02 is the first one since the Great American Total Eclipse of Such a close Moon during a total eclipse typically produces a long duration of totality - especially if the path passes near the Equator.
In the case of the July 02 event, the maximum duration is just over 4. The total eclipse is visible from within a narrow corridor that traverses the Pacific Ocean and southern South America. A partial eclipse is seen within the much broader path of the Moon's penumbral shadow, which includes the Pacific Ocean and most of South America Figure 3.
Oeno Island is a remote coral atoll and is part of the Pitcairn Islands. Unfortunately, there is no other landfall along the entirety of the Pacific track of kilometers.
Astronomy Calendar of Celestial Events - Sea and Sky
Greatest eclipse occurs at The path of totality finally reaches the coast of Chile at The region enjoys especially dry and clear weather - so much so that a string of major international astronomical observatories have been built there, including Cerro Tololo, La Silla and Gemini South. After crossing the Andes, the lunar shadow descends into Argentina for the last segment of its track.
The shadow covers the kilometer-stretch across Argentina in only 3 minutes. In Argentina, San Juan lies just inside the southern limit while Cordoba is 75 kilometers north of the track.
Just before the path ends, it barely misses Buenos Aires, the northern edge only 30 kilometers south of the center of the capital. Nevertheless, all roads leading from Buenos Aires to the central line will probably be clogged with traffic on eclipse day.
Central line coordinates and circumstances are presented in Table 3. Partial phases of the eclipse are visible across the southern Pacific Ocean and South America. Local circumstances for a number of cities in South America are found in Table 4. The Sun's altitude and azimuth, the eclipse magnitude and obscuration are all given at the instant of maximum eclipse at each location.
The Jul 02 Solar Eclipse Circumstances Calculator is an interactive web page that can quickly calculate the local circumstances for the eclipse from any geographic location not included in Table 4.
This is the 58th eclipse of Saros Espenak and Meeus, All eclipses in the series occur at the Moon's ascending node and gamma decreases with each member in the family. The series is a mature one that began with a modest partial eclipse on Oct After 20 partial eclipses in the series and more than 3 centuries, the first umbral eclipse occurred on May The event was a 2-minute total eclipse through New England, eastern Canada and Greenland.
During the next 2 centuries, the umbral duration continued to increase as each path shifted progressively southward. The greatest umbral duration of Saros occurred during the total eclipse of Aug Unfortunately, the 5 minute 40 second total eclipse was only visible from equatorial Africa, which was virtually inaccessible to astronomers of the day.
As the duration of each succeeding eclipse decreased, the paths reversed their southern migration and drifted northward during the 18th and 19th centuries. This effect occurred as a result of the Northern Hemisphere season shifting from winter to summer when the Northern Hemisphere tipped towards the Sun.
The southbound trend of the Saros series resumed with the eclipse of May At this point, the duration of totality at greatest eclipse had again increased to over 5 minutes. The most recent member occurred on Jun 21 and its path crossed southern Africa on the summer solstice.
After , the next member occurs on Jul 13 and passes through Australia and New Zealand. On Jul 24, the series returns to the African continent producing a path through South Africa.
The duration of totality drops as Saros continues to produce total eclipses during the 21st century. The last total eclipse of the series occurs on Aug 15 and lasts a maximum of 1 minute 38 seconds.
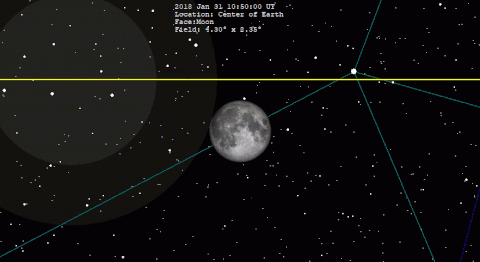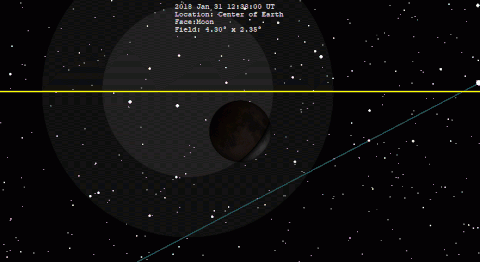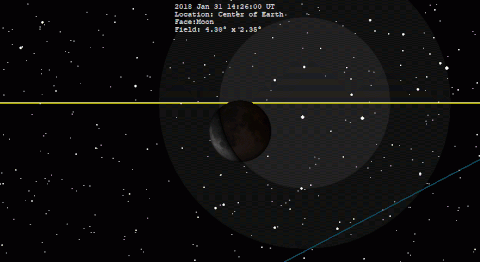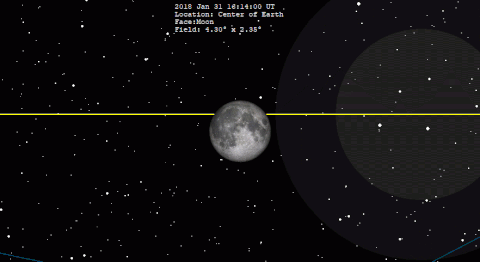
The final 20 eclipses of the series are all partial events in the polar regions of the Southern Hemisphere. The family terminates with the partial eclipse of Mar Click for detailed diagram Partial Lunar Eclipse of July It takes place 4.
At the instant of greatest eclipse The event is well placed for observers in Europe, Africa, and South Asia. None of the eclipse will be visible from North America. South America will see later stages of the eclipse, which begins before the Moon rises.
Table 5 lists predicted umbral immersion and emersion times for 25 well-defined lunar craters. The July 16 eclipse is the 21st eclipse of Saros This series began on Dec 09 and is composed of 79 lunar eclipses in the following sequence: The first total eclipse is on Aug 17 and the final eclipse of the series is on Apr Click for detailed diagram Annular Solar Eclipse of December The last eclipse of the year is the third solar eclipse.
A partial eclipse is visible from a much larger region covering much of Asia, northeast Africa, Oceana and western Australia Figure 6. The central path begins in Saudi Arabia about kilometers northeast of Riyadh at The path width is kilometers and the duration of annularity is 2 minutes 59 seconds. Although Bahrain lies just outside the path, the southern half of Qatar is within the path of annularity.
Continuing to the southeast, the path crosses the southern United Arab Emirates and northern Oman before entering the Arabian Sea. The antumbral shadow reaches the southwest coast of the Indian subcontinent at Traveling with a ground speed of about 1. It sweeps over northern Sri Lanka before heading into the Bay of Bengal.
Greatest eclipse occurs in eastern Sumatra at Racing across the South China Sea, the central track crosses Borneo and the Celebes Sea as it curves to the northeast and passes south of the Philippines archipelago. As it heads across the western Pacific, the antumbral shadow encounters Guam at 6: During the course of its 3.
Path coordinates and central line circumstances are presented in Table 6. Local circumstances and eclipse times for a number of cities in Asia are listed in Table 7.
The Sun's altitude and azimuth, eclipse magnitude and eclipse obscuration are all given at the instant of maximum eclipse. The December 26 Solar Eclipse Circumstances Calculator is an interactive web page that can quickly calculate the local circumstances for the eclipse from any geographic location not included in Table 7.
This is the 46th eclipse of Saros Espenak and Meeus, The series began on Aug 13 with a string of 20 partial eclipses. The series continued with 33 consecutive annular eclipses from Mar 17 to Mar Saros then changes character with 2 hybrid eclipses from Mar 23 to Apr The first of 7 total eclipses occurs on Apr Meteors will radiate from the constellation Lyra, but can appear anywhere in the sky.
May 4 - New Moon.
Categories
May 6, 7 - Eta Aquarids Meteor Shower. The Eta Aquarids is an above average shower, capable of producing up to 60 meteors per hour at its peak. Most of the activity is seen in the Southern Hemisphere. In the Northern Hemisphere, the rate can reach about 30 meteors per hour.
It is produced by dust particles left behind by comet Halley, which has known and observed since ancient times. The shower runs annually from April 19 to May It peaks this year on the night of May 6 and the morning of the May 7. The thin crescent moon will set early in the evening leaving dark skies for what should be a good show.
Meteors will radiate from the constellation Aquarius, but can appear anywhere in the sky. May 18 - Full Moon, Blue Moon. This full moon was known by early Native American tribes as the Full Flower Moon because this was the time of year when spring flowers appeared in abundance.
Since this is the third of four full moons in this season, it is known as a blue moon. But since full moons occur every The extra full moon of the season is known as a blue moon. Blue moons occur on average once every 2.
June 3 - New Moon. June 10 - Jupiter at Opposition.
Eclipses During 2019
The giant planet will be at its closest approach to Earth and its face will be fully illuminated by the Sun. It will be brighter than any other time of the year and will be visible all night long.
This is the best time to view and photograph Jupiter and its moons.

A medium-sized telescope should be able to show you some of the details in Jupiter's cloud bands. A good pair of binoculars should allow you to see Jupiter's four largest moons, appearing as bright dots on either side of the planet. June 17 - Full Moon. This full moon was known by early Native American tribes as the Full Strawberry Moon because it signaled the time of year to gather ripening fruit.
It also coincides with the peak of the strawberry harvesting season. June 21 - June Solstice. The June solstice occurs at The North Pole of the earth will be tilted toward the Sun, which will have reached its northernmost position in the sky and will be directly over the Tropic of Cancer at This is the first day of summer summer solstice in the Northern Hemisphere and the first day of winter winter solstice in the Southern Hemisphere.
June 23 - Mercury at Greatest Eastern Elongation. July 2 - New Moon. July 2 - Total Solar Eclipse. A total solar eclipse occurs when the moon completely blocks the Sun, revealing the Sun's beautiful outer atmosphere known as the corona. The path of totality will only be visible in parts of the southern pacific Ocean, central Chile, and central Argentina.
A partial eclipse will be visible in most parts of the southern Pacific Ocean and western South America. July 9 - Saturn at Opposition.
The ringed planet will be at its closest approach to Earth and its face will be fully illuminated by the Sun. This is the best time to view and photograph Saturn and its moons. A medium-sized or larger telescope will allow you to see Saturn's rings and a few of its brightest moons.
July 16 - Full Moon. This full moon was known by early Native American tribes as the Full Buck Moon because the male buck deer would begin to grow their new antlers at this time of year. July 16 - Partial Lunar Eclipse. A partial lunar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes through the Earth's partial shadow, or penumbra, and only a portion of it passes through the darkest shadow, or umbra.
During this type of eclipse a part of the Moon will darken as it moves through the Earth's shadow. July 28, 29 - Delta Aquarids Meteor Shower. The Delta Aquarids is an average shower that can produce up to 20 meteors per hour at its peak.
It is produced by debris left behind by comets Marsden and Kracht. The shower runs annually from July 12 to August It peaks this year on the night of July 28 and morning of July The waning crescent moon will not be too much of a problem this year. The skies should be dark enough for what could be a good show.
- 1. Let go of the ego..
- Table of Eclipse Dates from to - Susan Miller Astrology Zone.
- Eclipses: Tables!
August 1 - New Moon. August 9 - Mercury at Greatest Western Elongation. August 12, 13 - Perseids Meteor Shower. The Perseids is one of the best meteor showers to observe, producing up to 60 meteors per hour at its peak. It is produced by comet Swift-Tuttle, which was discovered in The Perseids are famous for producing a large number of bright meteors.
The shower runs annually from July 17 to August It peaks this year on the night of August 12 and the morning of August The nearly full moon will block out most of the fainter meteors this year, but the Perseids are so bright and numerous that it could still be a good show.
Meteors will radiate from the constellation Perseus, but can appear anywhere in the sky. August 15 - Full Moon.
This full moon was known by early Native American tribes as the Full Sturgeon Moon because the large sturgeon fish of the Great Lakes and other major lakes were more easily caught at this time of year.
August 30 - New Moon. September 9 - Neptune at Opposition. The blue giant planet will be at its closest approach to Earth and its face will be fully illuminated by the Sun. This is the best time to view and photograph Neptune.
Due to its extreme distance from Earth, it will only appear as a tiny blue dot in all but the most powerful telescopes. September 14 - Full Moon. This full moon was known by early Native American tribes as the Full Corn Moon because the corn is harvested around this time of year.
This moon is also known as the Harvest Moon. The Harvest Moon is the full moon that occurs closest to the September equinox each year. September 23 - September Equinox. The September equinox occurs at This is also the first day of fall autumnal equinox in the Northern Hemisphere and the first day of spring vernal equinox in the Southern Hemisphere.
September 28 - New Moon. October 8 - Draconids Meteor Shower. The Draconids is a minor meteor shower producing only about 10 meteors per hour. It is produced by dust grains left behind by comet 21P Giacobini-Zinner, which was first discovered in The Draconids is an unusual shower in that the best viewing is in the early evening instead of early morning like most other showers.
The shower runs annually from October and peaks this year on the the night of the 8th. The first quarter moon will set shortly after midnight leaving fairly dark skies for observing. Best viewing will be in the early evening from a dark location far away from city lights.
Meteors will radiate from the constellation Draco, but can appear anywhere in the sky. October 13 - Full Moon. This full moon was known by early Native American tribes as the Full Hunters Moon because at this time of year the leaves are falling and the game is fat and ready to hunt.
This moon has also been known as the Travel Moon and the Blood Moon. October 20 - Mercury at Greatest Eastern Elongation. October 21, 22 - Orionids Meteor Shower. The Orionids is an average shower producing up to 20 meteors per hour at its peak. It is produced by dust grains left behind by comet Halley, which has been known and observed since ancient times.
The shower runs annually from October 2 to November 7. It peaks this year on the night of October 21 and the morning of October The second quarter moon will block some of the fainter meteors this year, but the Orionids tend to be fairly bright so it could still be a good show.
Meteors will radiate from the constellation Orion, but can appear anywhere in the sky. October 27 - Uranus at Opposition. The blue-green planet will be at its closest approach to Earth and its face will be fully illuminated by the Sun.
This is the best time to view Uranus. Due to its distance, it will only appear as a tiny blue-green dot in all but the most powerful telescopes. October 28 - New Moon. November 5, 6 - Taurids Meteor Shower. The Taurids is a long-running minor meteor shower producing only about meteors per hour.
It is unusual in that it consists of two separate streams. The first is produced by dust grains left behind by Asteroid TG The second stream is produced by debris left behind by Comet 2P Encke.
The shower runs annually from September 7 to December It peaks this year on the the night of November 5. The first quarter moon will set shortly after midnight leaving dark skies for viewing.
Best viewing will be just after midnight from a dark location far away from city lights. Meteors will radiate from the constellation Taurus, but can appear anywhere in the sky. The planet Mercury will move directly between the Earth and the Sun.
Viewers with telescopes and approved solar filters will be able to observe the dark disk of the planet Mercury moving across the face of the Sun.
This is an extremely rare event that occurs only once every few years. The next transit of Mercury will not take place until The best place to view this event in its entirety will be the eastern United States, Central America, and South America.
Transit Visibility Map and Information. November 12 - Full Moon. This full moon was known by early Native American tribes as the Full Beaver Moon because this was the time of year to set the beaver traps before the swamps and rivers froze.
It has also been known as the Frosty Moon and the Hunter's Moon. November 17, 18 - Leonids Meteor Shower.
- aries aries cusp sign compatibility?
- birthday number 16 meaning.
- weekly horoscope sagittarius february 17 2019;
- Mars enters Aries.
- cancer horoscope born january 21?
- 7 january horoscope pisces?